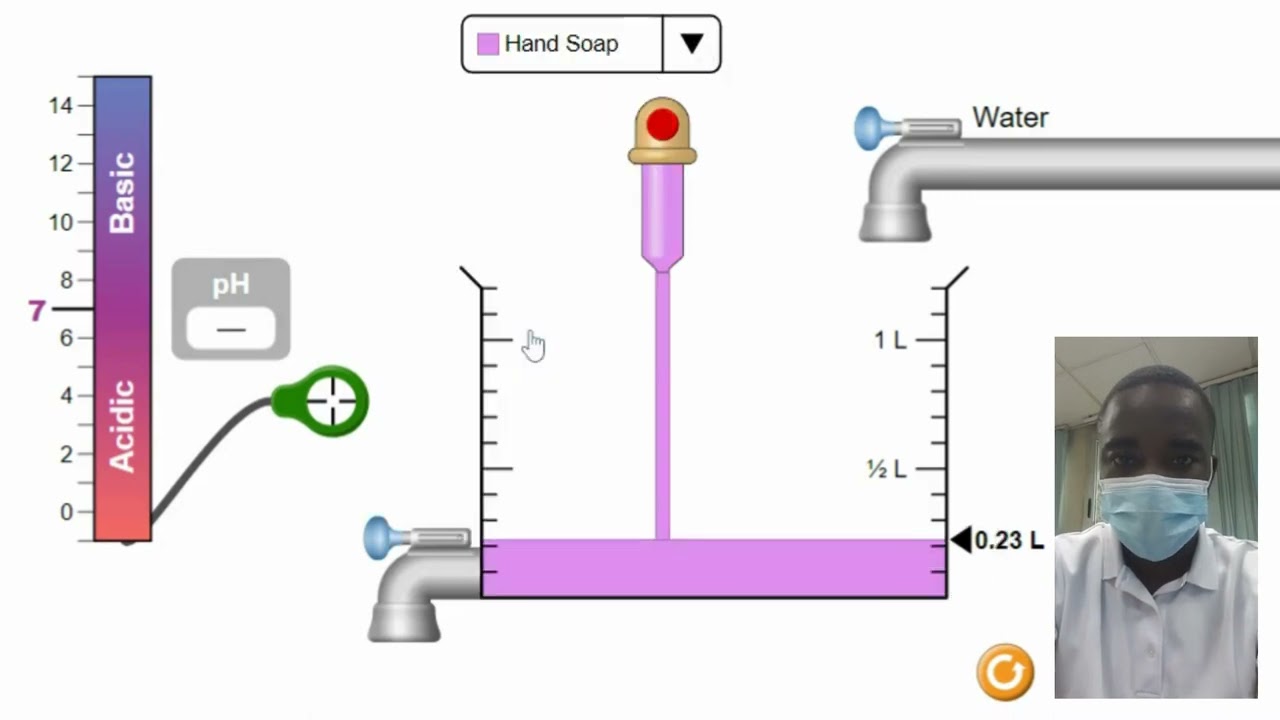
Have you ever wondered how scientists determine the acidity or basicity of a substance? The pH scale is a crucial tool in the world of chemistry that allows us to understand the relative concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. In this article, we will delve into the exciting realm of the pH scale, but with a twist – we will explore it through the lens of a virtual lab experience. Get ready to dive into the fascinating world of acidity and basicity with our virtual lab pH scale adventure!
Introduction: Unveiling the Mysteries of the pH Scale
Before we embark on our virtual lab journey, let’s take a moment to understand what the pH scale is all about. The pH scale is a logarithmic scale that measures the acidity or basicity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are considered acidic, while those with a pH greater than 7 are considered basic. The pH scale provides scientists with a standardized way to quantify the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution.
Exploring the Virtual Lab: A Hands-On Experience
Now that we have a grasp of what the pH scale entails, let’s step into the virtual lab and put our knowledge to the test. In this virtual lab, you will have the opportunity to experiment with various substances and determine their pH levels. Strap on your scientific goggles, grab your lab coat, and let’s dive in!
Getting Started: Gathering the Necessary Tools
Before we begin our experiments, we need to gather the essential tools for our virtual lab. In the virtual lab interface, you will find a wide array of substances, test tubes, and a pH meter. Our first task is to select the substances we want to test. You can choose from a range of options, including household items like lemon juice, vinegar, and baking soda. Once you have selected your substances, it’s time to move on to the next step.
Conducting the Experiments: Unleashing Your Inner Scientist
Now that we have our substances ready, it’s time to conduct the experiments. In the virtual lab, you can pour each substance into separate test tubes and insert the pH meter to measure their pH levels. As you observe the pH meter readings, you will notice that each substance falls into a specific range on the pH scale. Lemon juice, for example, is known to be acidic, so it will likely have a pH below 7. On the other hand, baking soda is basic, so its pH will be above 7. Don’t forget to take notes as you go along, documenting your findings and observations.
Analyzing the Results: Decoding the pH Scale
Once you have completed your experiments, it’s time to analyze the results and decode the pH scale. Take a moment to compare the pH values of the different substances you tested. You will notice that each substance falls into a specific category on the pH scale. Substances with a pH below 7 are acidic, while those with a pH above 7 are basic. The closer a substance’s pH is to 0 or 14, the more acidic or basic it is, respectively. For example, a substance with a pH of 1 is highly acidic, while a substance with a pH of 13 is highly basic. Keep in mind that the pH scale is logarithmic, meaning that each unit represents a tenfold difference in acidity or basicity.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: Can I conduct these experiments at home?
A: While the virtual lab provides a safe and educational experience, it’s important to note that conducting experiments involving chemicals at home can be hazardous. It’s always best to leave such experiments to professionals or educational institutions with proper safety measures in place.
Q: How is the pH scale relevant to everyday life?
A: The pH scale has numerous real-world applications. It helps in various industries, such as agriculture, where the pH of soil determines its suitability for different crops. Additionally, the pH scale is crucial in the field of medicine, as it aids in the diagnosis and treatment of various conditions.
Q: Are there substances that fall outside the pH scale range?
A: While the pH scale typically ranges from 0 to 14, there are some substances that can have pH values beyond this range. For example, highly concentrated sulfuric acid can have a pH of less than 0, while certain concentrated alkaline solutions can have a pH greater than 14.
Conclusion: Unleashing Your Inner Chemist
Congratulations! You have successfully completed your virtual lab pH scale adventure. Through this immersive experience, you have gained a deeper understanding of the pH scale and its role in determining the acidity or basicity of substances. Remember, the pH scale is not just a theoretical concept – it has practical applications in various fields, from agriculture to medicine.
So, the next time you come across a lemon or a bottle of vinegar, you can impress your friends with your knowledge of the pH scale. Go forth and unleash your inner chemist, armed with the power of the virtual lab pH scale!
Now that you’ve explored the virtual lab pH scale, it’s time to take what you’ve learned and apply it to the world around you. Whether you’re testing the pH of your morning cup of coffee or investigating the acidity of rainwater, the pH scale offers a fascinating insight into the chemical properties of our everyday lives. So, grab your lab coat, put on your scientific thinking cap, and let the virtual lab pH scale adventure begin!