Have you ever wondered how substances move across a cell membrane? How do nutrients enter our cells and waste products exit? The answer lies in the fascinating processes of diffusion and osmosis. These invisible forces play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance within our bodies. In this article, we will explore the concept of diffusion and osmosis through the lens of a virtual lab. So, grab your lab coat and let’s dive into the intriguing world of diffusionosmosis!
The Basics of Diffusion
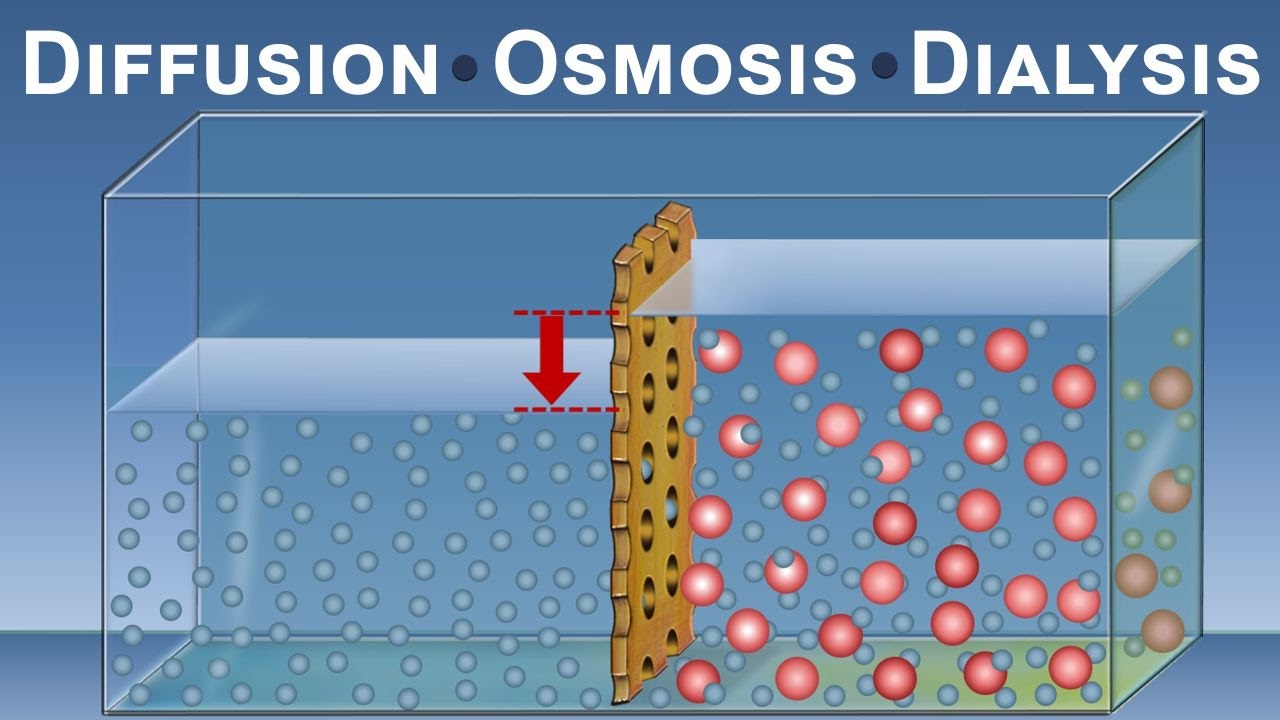
Diffusion is like a party for molecules. It’s a process where molecules spontaneously move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Picture a crowded dance floor where everyone wants their own space. Eventually, people start to diffuse and spread out, creating more space for everyone. Similarly, molecules in a concentrated area want to spread out evenly, seeking equilibrium.
In the virtual lab, we observed the diffusion of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) through a semi-permeable membrane. This membrane allows certain molecules to pass through while restricting others. By measuring the rate of diffusion, we can determine how different factors affect the process.
Factors Affecting Diffusion
-
Temperature: Just like people get more energetic in a warm room, molecules also move faster at higher temperatures. This increased movement leads to faster diffusion. In our virtual lab, we observed that as we increased the temperature, the rate of diffusion of KMnO4 also increased. This suggests that temperature plays a significant role in the speed of diffusion.
-
Molecular Size: Size matters, even in the world of molecules! Smaller molecules diffuse more quickly because they can squeeze through the tiny gaps in the membrane. In contrast, larger molecules struggle to pass through, slowing down the diffusion process. Our virtual lab confirmed this hypothesis, as we observed that smaller molecules diffused faster compared to larger ones.
-
Concentration Gradient: Imagine a room with a strong perfume. As you move away from the source, the scent becomes weaker. Similarly, the concentration gradient is the difference in concentration between two areas. The steeper the gradient, the faster diffusion occurs. In our virtual lab, we manipulated the concentration gradient by changing the initial concentration of KMnO4. As expected, a higher concentration led to faster diffusion.
Understanding Osmosis
Now that we’ve explored the world of diffusion, let’s dive into the captivating process of osmosis. Osmosis is a special type of diffusion that involves the movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane. Like a thirsty person reaching for a glass of water, cells need to maintain their water balance to stay healthy.
In our virtual lab, we examined the osmosis of water across a potato cell membrane. By immersing potato slices in solutions of varying concentrations, we observed the effects of osmosis on the cells.
Impact of Solute Concentration
Solute concentration plays a pivotal role in osmosis. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution (lower solute concentration outside the cell), water rushes into the cell, causing it to swell. It’s like a balloon being filled with air!
Conversely, when a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution (higher solute concentration outside the cell), water rushes out of the cell, causing it to shrink and become dehydrated. It’s like a deflated balloon losing air!
In our virtual lab, we observed the changes in potato slice size as it went through these different osmotic scenarios. The results aligned with our understanding of osmosis, proving that water moves across a semi-permeable membrane to equalize solute concentrations.
FAQs
Q: How are diffusion and osmosis different?
A: Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration, while osmosis specifically refers to the movement of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane.
Q: What is a semi-permeable membrane?
A: A semi-permeable membrane is a barrier that allows certain molecules or ions to pass through while restricting others.
Q: Why is osmosis important in biology?
A: Osmosis is crucial for maintaining the balance of water and solutes in cells. It ensures that cells remain hydrated and function properly.
Conclusion
In this virtual lab, we’ve explored the fascinating processes of diffusion and osmosis. We’ve witnessed the movement of molecules and water across semi-permeable membranes, unraveling the mysteries of these invisible forces. From the impact of temperature and molecular size on diffusion to the effects of solute concentration on osmosis, we’ve gained valuable insights into how substances move within living organisms.
By understanding diffusion and osmosis, we can better comprehend the intricate workings of our own bodies. These processes are vital for the survival and proper functioning of cells. So, the next time you take a sip of water or enjoy a nutritious meal, remember the remarkable dance of diffusionosmosis happening within you. It’s a continual symphony of molecules, keeping you alive and thriving!